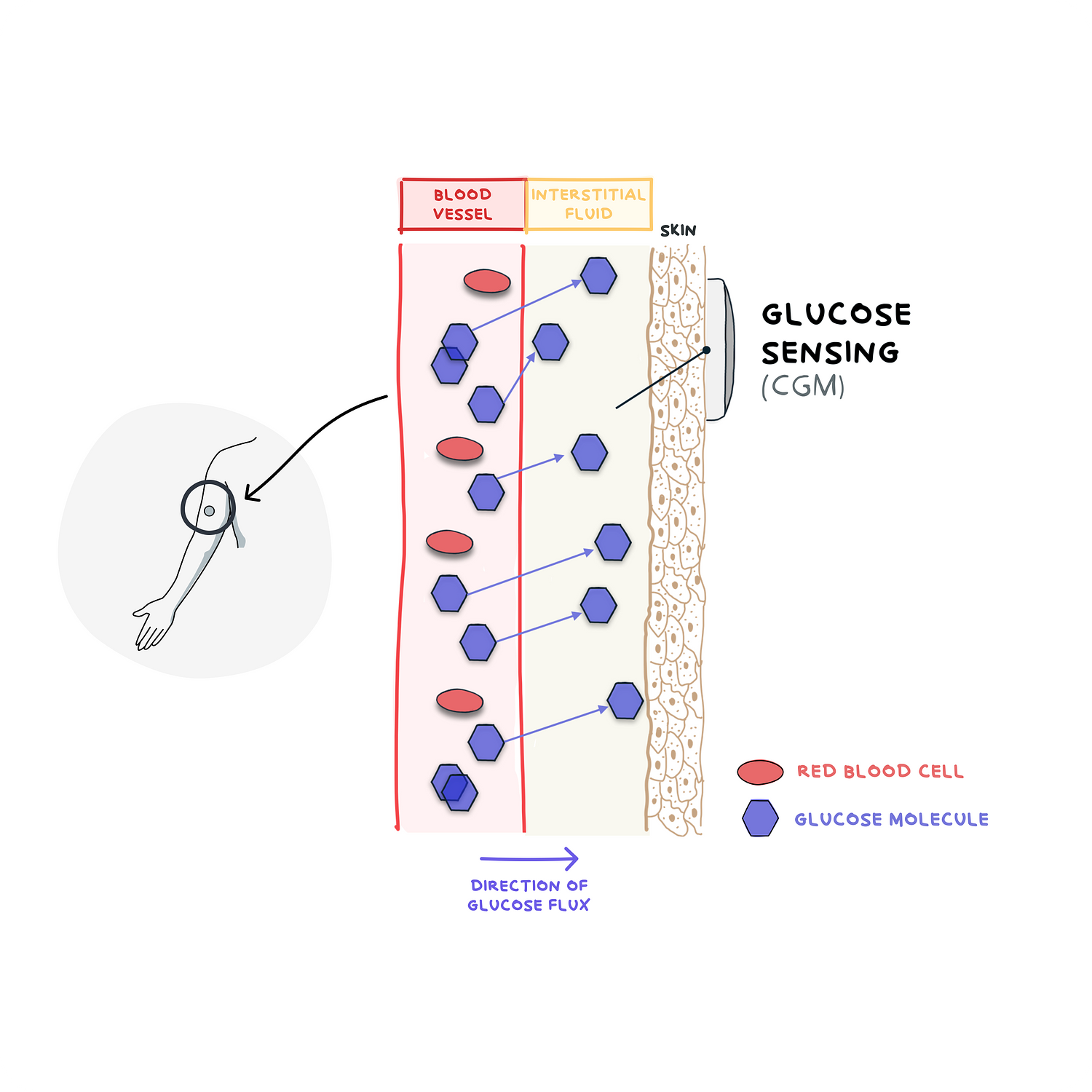
Figure 6. How CGMs Work: Tracking Glucose Levels. A visual illustration of the flow of glucose from the blood into the interstitial fluid that is detected by the CGM sensor and then transmitted to the receiver. CGM sensors are inserted subcutaneously (under the skin) with a fine needle and provide interstitial glucose values 24 hours a day, measuring every 1-5 minutes. They come with alerts for high or low glucose levels and glucose trend information 73. This allows users to monitor their glucose levels without the need for fingerstick tests, and CGM use has been shown to improve diabetes management, as reflected by decreases in HbA1c after 6 months 75.